News Letter, Vol. 3 (12), December, 2011, © Copyright
Jun Xu, M.D. Lic. Acup., Hong Su, C.M.D., Lic. Acup.
Robert Blizzard III, DPT
Rehabilitation Medicine and Acupuncture Center
1171 East Putnam Avenue, Building 1, 2nd Floor
Greenwich, CT 06878
Tel: (203) 637-7720
Wrist Pain after Bike Riding- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
photography.nationalgeographic.com
Derek is 43 year-old male, who likes to cycle cross country. He has regularly biked 100 miles per week for over 10 years. On weekends he will get up early in the morning and get in a very intensive bike ride. About 2 months ago, he started to feel both hands had weakness and tenderness along with numbness and a tingling sensation bilaterally at the 4th and 5th fingers. He even felt coldness at the 4th and 5th fingers. He sometimes has difficulty typing, and has to shake his hands to rid of numbness after waking up from sleep. He visited his primary care physician, and was given Advil for his pain and told that after a few weeks the pain and numbness might go away. However, he still feels it and is getting worse, therefore, he comes to me for evaluation and treatment.
Because the 4th and 5th fingers are supplied with ulnar nerve, therefore, his symptom made me think ulnar nerve entrapment, i.e. Guyon’s canal syndrome. By physical examination, the patient had weakness to make a full fist, and weaker to spread out his 5 fingers.
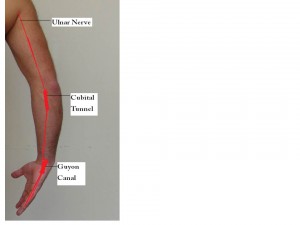
The ulnar nerve is one of the three main nerves in the arm. Ulnar nerve is located underneath the shoulder, arm and little and ring fingers. Along its pathway, there are a few locations the ulnar nerve is easily trapped. As indicated at this figure.
Fig 12.1
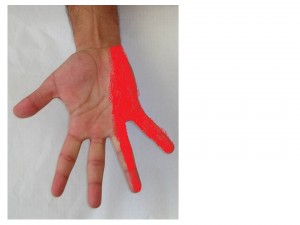
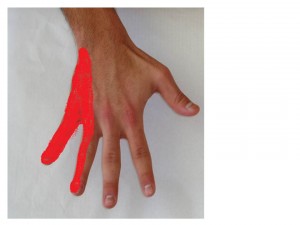
The ulnar nerve functions to give sensation to the little finger and the half of the ring finger that is near the little finger. It also controls most of the little muscles in the hand that help with fine movements, and some of the bigger muscles in the forearm that help to make a strong grip.
Fig 12.2
Fig 12.3
- The cubital tunnel: Ulnar nerve travels from under the collarbone and along the inside of the upper arm. It passes through a tunnel of tissue (the cubital tunnel) behind the inside of the elbow. While holding your elbow on the desk such as answering your phone, or when lying on your stomach by holding your arm face down, one sometimes feels the funny sensation commonly called the “funny bone.”
Fig 12.4
- Guyon’s canal : Beyond the elbow, the nerve travels under muscles on the inside of the arm and into the hand on the side of the palm with the little finger. As the nerve enters the hand, it travels through another tunnel (Guyon’s canal). The most common injury is by riding a bicycle for long time, like the above case.
Fig 12.5
http://www.hughston.com/hha/a_15_3_2.htm
Presenting symptoms of ulnar nerve entrapment can vary from mild transient pins and needles sensation, i.e. paraesthesias in the ring and small fingers to clawing of these digits and severe intrinsic muscle atrophy.The patient may report severe pain at the elbow or wrist with radiation into the hand or up into the shoulder and neck. Patients may report difficulty opening jars, spreading out hand and fingers or turning door knobs. The patients may feel early fatigue or weakness after repetitive hand motions, such as typing, sorting mails, etc. increasing numbness and paraesthesias may be noticed throughout the day.
Ulnar neuropathy can be caused by nerve damage, which can result from inflammation or compression along the pathway of ulnar nerve:
- Ulnar nerve at or near the elbow
- Compression at work, sleep or during general anesthesia
- Blunt trauma
- Malnutrition leading to muscle atrophy and loss of fatty protection across the elbow and other joints
- Deformities (eg, rheumatoid arthritis, fracture of elbow bones)
- Metabolic derangements (eg, diabetes)
- Venipuncture
- Hemophilialeading to hematomas
- Ulnar neuropathy at or distal to the wrist (ie, at Guyon’s canal)
- Bicycle
- Tumors
- Ganglionic cysts
- Blunt injuries with or without fracture
- Idiopathic
Diagnosis:
Proper diagnosis of ulnar nerve entrapment depends on an experienced physician:
· Clear medical history taken, your physician should ask you in detail, including when, where, how, the symptom started, etc.
· A comprehensive medical examination, including, inspection of any muscle atrophy, palpation of the tender area, range of motion, sensitivity, special muscle strength test, etc.
- Electrodiagnostic studies (EMG) to study nerve conduction within your hands and wrists, which is a gold standard for final diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy
Treatment:
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of your symptom. For mild to moderate ulnar neuropathy, conservative treatment, such as physical/occupational therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine, splints and acupuncture are recommended.
- Physical Therapy to stretch, strengthen and remove adhesions in the ligaments and tendons in the hands and elbows
- Ulnar Nerve Gliding: perform this maneuver till the hand is upside down with the fingers around the eye as shown below. Hold for 20 seconds x 3 reps.
Fig 12.6
- The daily use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and other nonprescription pain relievers to help reduce pain and inflammation
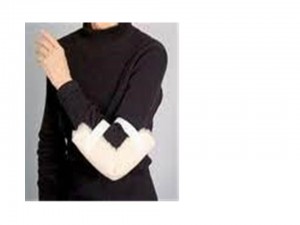
- Wearing splints to help immobilize and protect the elbow and wrist
Fig 12.7
www.fairtrade-advocacy.org
- Acupuncture
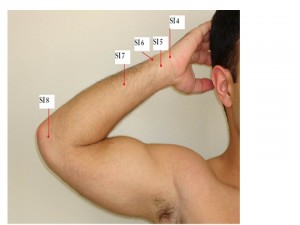
The most commonly used points are the following:
SI 4 Wan Gu, SI 5 Yang Gu, SI 6 Yang Lao, SI 7 Zhi Zheng, SI 8 Xiao Hai
| Points | Meridian/No. | Location | Function/Indication | |
| 1 | Wan Gu | SI 4 | On the ulnar side of the palm, in the depression between the base of the fifth metacarpal bone and the triquetral bone | Febrile diseases with anhidrosis, headache, rigidity of the neck, contracture of the fingers, pain in the wrist, jaundice |
| 2 | Yang Gu | SI 5 | At the ulnar end of the transverse crease on the dorsal aspect of the wrist, in the depression between the styloid process of the ulnar and the triquetral bone. | Swelling of the neck and submandibular region, pain of the hand and wrist, febrile diseases |
| 3 | Yang Lao | SI 6 | Dorsal to the head of the ulna. When the palm faces the chest, the point is in the bony cleft on the radial side of the syloid process of the ulna. | Blurring of vision, pain in the shoulder, elbow and arm |
| 4 | Zhi Zheng | SI 7 | On the line joining SI 5 Yang Gu and SI 8 Xiao Hai, 5 inch above Yang Gu | Neck rigidity, headache, dizziness, spasmodic pain in the elbow and fingers, febrile diseases, mania |
| 5 | Xiao Hai | SI 8 | When the elbow is flexed, the point is located in the depression between the olecranon of the ulna and the medical epcondyle of the humerus | Headache, swelling of the cheek, pain in the shoulder, arm and elbow, epilepsy |
Fig 12.8
- Surgery: for severe cases and after the above conservative treatment, the following methods are considered:
- At the elbow. Your surgeon will make an incision at the elbow and perform a nerve decompression. Or your surgeon may choose to move the nerve to the inner part of the arm so that it is in a more direct position.
- At the wrist. If the compression is at the wrist, the incision is made there and the decompression is performed.
Tips for Acupuncturists:
- Make a clear diagnosis, check the causes of ulnar neuropathy, acupuncture may not change the causes of the disease
- Early treatment will help the course, however, acupuncture only may help for the symptom, patients have to change their practice of sports or working
Tips for Patients:
- Avoid press your elbow and wrist during sports or work.
- Temporary numbness and tingling sensation at ring and little fingers usually will disappear without treatment. However, if you constantly press your elbow and wrist, you may have permanent damage.





One comment
digestive drink
January 20, 2015 at 11:18 am
Yes! Finally something about side effects.