News Letter, Vol. 3 (4), April, 2011, © Copyright
Jun Xu, M.D. Lic. Acup., Hong Su, C.M.D., Lic. Acup.
Robert Blizzard III, DPT
Rehabilitation Medicine and Acupuncture Center
1171 East Putnam Avenue, Building 1, 2nd Floor
Greenwich, CT 06878
Tel: (203) 637-7720 begin_of_the_skype_highlighting (203) 637-7720 end_of_the_skype_highlighting
Knee Pain and Knee Osteoarthritis
thisdayinquotes.com
Jonathan S. a 44-year-old man has experienced knee pain on and off for two years. He played varsity football while in college and after graduation took up tennis which he played often over the years, four or more times a week, and never had a physical problem. However, the knee pain developed two years ago and the symptoms become worse with weather changes. His pain has been getting worse, even when he is only walking and he has stiffness and swelling, with decreased range of motion when he wakes up in the morning. He experiences difficulty bending or extending his knee and when he goes up or downstairs, he feels as his right knee is giving out. He has severe tenderness along the joint, so he consulted his primary care physician who suspected osteoarthritis of the right knee. When an X-ray was done it showed his right knee cartilage was worn out and the knee joint had a very narrow space. Jonathan was told osteoarthritis of the knee and it was a very serious condition and the best way to treat it would be with a total knee replacement, which he refused to do.
He then consulted me and I noted his knee was moderately swollen and when I checked the range of motion there was limited knee flexion (about 0-70 degrees) . When I moved the knee I heard clicking and cracking noises, which indicated crepitation of the right knee. I also checked the knee X-ray which showed the knee space narrowing and also noted some bony spurs along the tibia and fibula bones, all of which confirmed the diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis.
What is Knee osteoarthritis?
Knee Osteoarthritis is caused by the breakdown and eventual loss of the cartilage of knee joint. Cartilage is a protein substance that serves as a “cushion” between the bones of the joints. Osteoarthritis is also known as degenerative arthritis, i.e. the wearing out of joints during aging process, the older, the worse the arthritis. Before age 45, osteoarthritis occurs more frequently in males. After 55 years of age, it occurs more frequently in females.
As we look at the following picture, the left side knee joint revealed severe OA with narrow space, in the following picture of the knees, the right one is a normal X-ray with plenty of knee space. The left one is a typical osteoarthritis knee. You will see the detail analysis or illustration of the left knee of the x-ray afterwards.
Fig. 4.1
https://sites.google.com/a/bishopfoley.org/anatomy-bfc/
Causes of Knee Osteoarthritis
As we mentioned above, deterioration of articular cartilage is the main problem associated with knee osteoarthritis. The condition can be caused by:
- Previous knee injury: Injuries contribute to the development of osteoarthritis. Fractures, ligament tear, and meniscal injury which can affect alignment and promote wear and tear. For example, athletes who have right knee-related injuries may try to avoid right knee pain by leaning to the left side, then he will be at higher risk of developing osteoarthritis of left knee.
- Repetitive strain on the knee: Overuse of certain joints increases the risk of developing osteoarthritis. For example, marathon runners, tennis players and football players are at increased risk for developing osteoarthritis of the knee.
- Genetics: Some people have an inherited defect in one of the genes responsible for making cartilage. This causes defective cartilage, which leads to more rapid deterioration of joints. People born with with an abnormality of the spine (such as scoliosis or curvature of the spine) are more likely to develop osteoarthritis of the spine and knee because of the change of dynamic chain in entire body.
- Obesity: Overweight increases the risk for osteoarthritis of the knee and hip by addition of stress and impact on the joint surface during weight bearing mobility. Maintaining ideal weight or losing excess weight may help prevent osteoarthritis of the knee and hip or decrease the rate of progression once osteoarthritis is established.
How Is Osteoarthritis Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis is based on a combination of the following factors:
1. Your description of symptoms includes: older than 40 years, knee Pain, Stiffness Decreasing range of motion, Muscle weakness and atrophy due to inactivity or stiffness, Baker’s cyst (a harmless fluid collection in the back of knee)
2. The location and pattern of pain: the pain located at the midline of the knee, morning stiffness, the pain follows weather changes sometimes
3. Certain findings of a physical exam: Crepitus, Effusion, Deformity, etc.
4. X-ray of the knee osteoarthritis includes the following characters:
* Joint Space Narrowing: Joint space loss is usually not uniform within the joint, the weight bearing part of the knee joint usually wear out more, “Bone-on-bone” suggests there is no joint space left.
* Development of Osteophytes: also called bone spurs, are protrusions of bone and cartilage, which typically develop as a reparative response by remaining cartilage, cause pain and limited range of motion in the affected joint.
* Subchondral Sclerosis: subchondral bone is the layer of bone just below the cartilage. Sclerosis means that there is hardening of tissue. Subchondral sclerosis is seen on x-ray as increased bone density, frequently found adjacent to joint space narrowing. The degeneration of bone which occurs in osteoarthritis causes bone to turn into a dense mass at the articular surfaces of bone.
* Subchondral Cyst Formation: are fluid-filled sacs which extrude from the joint. The cysts contain thickened joint material, mostly hyaluronic acid. Traumatized subchondral bone undergoes cystic degeneration.
5. Sometimes blood tests will be given to determine if you have a different type of arthritis.
6. If fluid has accumulated in the joints, your doctor may remove some of the fluid (called joint aspiration) for examination under a microscope to rule out other diseases.
Treatment of the knee by western medicine.
For all knee pain, the most important thing is to divide the pain into two types:
- Acute stage. In this stage the patient suffered a trauma or injury with acute pain, so it is necessary to use acronym PRICE measures for this stage.
- Protection. Use or crutches or a brace is necessary to help stabilize the joint to avoid weight bearing and prevent further damage.
- Rest. Reduce or stop the activities that caused the pain, which will help reduce the pain and improve the injury.
- Ice. In the acute stage, there is pain and acute inflammation. Ice will decrease this inflammation and should be applied to the injured knee three or four times a day for 20 minutes at a time. It also helps to rub the ice pack around the knee to protect the knee and decrease the pressure of the inflammation.
- Compression. Use of a compression bandage and massaging the damaged tissue helps to prevent fluid build up edema, and hard rubbing of the knee helps to strengthen it.
- Elevation. Elevate your leg with help of gravity will facilitate the fluid return from the swelling knee to your heart, which will decrease the knee swelling.
- Postacute Stage. For mild to moderate knee pain, the following can help:
- Anti-inflammatory medication. Non-steroid anti-inflammatory medication such as NSAID’s, including asperin, nanproxen and ibuprofen help decrease the inflammation and decrease the pain.
- Physical therapy. The proper exercises will strengthen the muscles around the knee and help to regain the knee stability.
A Foam Roller, Hand Held Marathon Massage Stick, or other types of Soft Tissue Work will assist in loosening adhesions and imbalances that may place greater stress through the joints of the knee and limit full range of motion of the muscles.
Fig. 4.2
http://www.sideofsneakers.com/2010/09/01/foam-roller-vs-the-stick/
Fig 4.3
http://zealousvitality.wordpress.com/tag/quads/
Fig. 4.4
http://www.h3daily.com/fitness/roll-it-out/
The muscles of the hip and knee must be strengthened with exercises placing less stress through the arthritic joint with Non-Weight Bearing (NWB) Exercises. 4-Way Hip Exercises on a mat will strengthen muscles surrounding the hip and knee. These should be progressed from 3 sets of 10, to 2 sets of 15 to 1 set of 30 then repeated with ankle weights.
Hip Flexion involves lying on your back with one knee bent and the working leg straight being lifted up to the height of the opposite knee than down slowly.
Hip Extension involves lying on your stomach and lifting one leg up about 10-12” then down slowly.
Hip Abduction and Hip Adduction both involve lying on your side. Hip Abduction involves the top leg being lifted up around 20” then down slowly. Hip Adduction involves crossing the top leg over the bottom leg and performing the exercise by lifting the bottom leg off the table about 10” then down slowly.
4-Way Hip Exercises on Mat
Fig. 4.5
http://www.sportsinjuryclinic.net/cybertherapist/corestability.php
http://www.best-leg-exercises.com/ankle-weights.html
Clam Shells are NWB and can be performed in a seated position or lying on your side to strengthening the muscles of the outer and inner thigh. Increased tension of the band will make the movement more challenging, select a band resistance to make the last few reps more difficult to achieve 2 sets of 10, then once able to complete a 3rd set, increase resistance.
Clam Shells Seated
Fig. 4.6
http://www.exercise.com/exercise/band-assisted-seated-hip-abduction
Fig. 4.7
Clam Shells Side Lying
http://www.active.com/cycling/Articles/Tight-IT-Band-3-Simple-Exercises-to-Fix-it-Now.htm?page=2
Utilizing a Stretch-Out Strap Routine following strengthening exercises will improve mobility in the muscles. Each stretch should be held from 30-60 seconds and repeated on both legs. This routine flows easy from one move to another and is NWB so less stress is placed through the knee joint compared to if these exercises were performed in standing.
Stretch-Out Strap Calves – place band around ball of foot and pull band back keeping knee straight till a strong but comfortable stretch is felt in the calves
Fig. 4.8
http://sicksport.com/fitness-stretching-c-86_111/stretch-out-strap-with-book-p-1361
Stretch-Out Strap Hamstrings – lie back and lift leg up keeping straight at knee till a strong but comfortable stretch is felt in hamstrings
Fig. 4.9
http://www.procombinetraining.com/pct_store.htm
Stretch-Out Strap Glutes – place band around shin and pull up towards chest till a strong but comfortable stretch is felt in the glute
Fig. 4.10
http://www.exf-fitness.com/en/products/10/90/Stretch_Out_Strap.aspx
Fig. 4.11
Stretch-Out Strap Inner Thigh – bring leg out to the side, keeping it off the ground till a strong but comfortable stretch is felt in the inner thigh
http://jones-strength.blogspot.com/
Fig. 4.12
http://jones-strength.blogspot.com/
Stretch-Out Strap Outer Thigh – bring leg across the body, keeping if off the ground till a strong but comfortable stretch is felt in the outer thigh
Stretch-Out Strap Quadriceps – lying on stomach with band around ankle, pull strap over shoulder till a strong but comfortable stretch is felt in the quadriceps
Fig. 4.13
http://www.simplefitnesssolutions.com/stretch.htm
Manual PT with supervised exercise has been shown beneficial with OA of knee and may prevent and delay surgical intervention
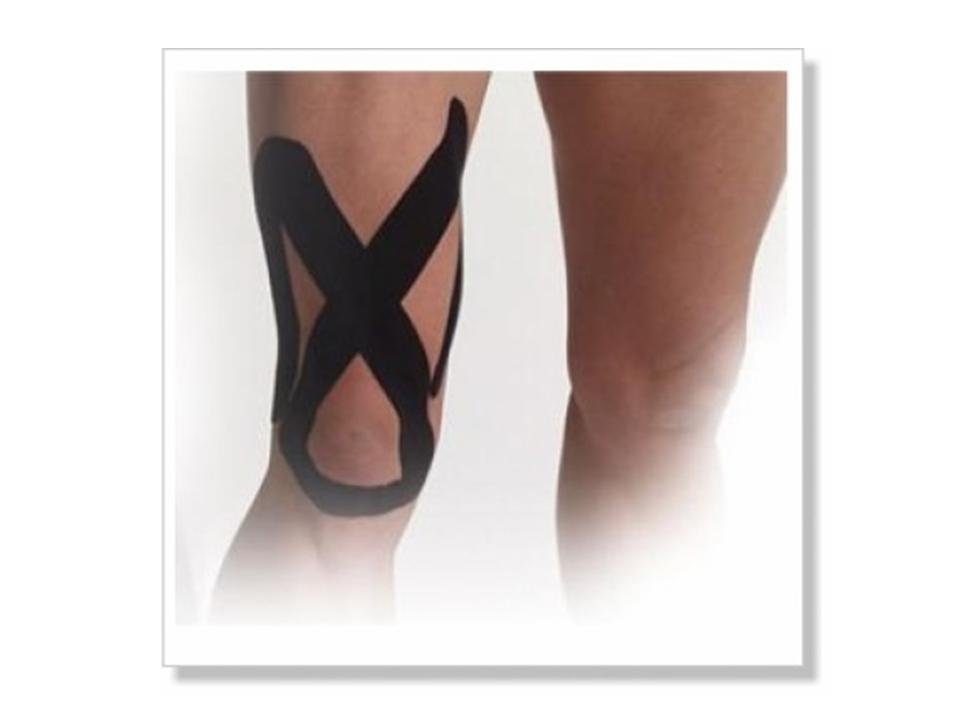
Recent research studies have shown benefits with Kinesio Taping to help reduce knee pain and improve quadriceps strength. The tape will assist in correcting imbalances at the knee to reduce stress on joints and recruit greater muscle activation.
Fig. 4.14
http://www.theratape.com/spidertech-precut-upper-knee-tape.html
Walking when pain free is a great form of exercise. Avoid high impact activities such as jogging and running and opt for walking, elliptical, exercise bike, swimming to improve the strength and range of motion of the leg muscles.
Fig. 4.15
http://www.healthcentral.com/chronic-pain/h/what-causes-knee-pain-when-walking.html
- Corticosteroid injections: steroid injection can quickly decrease the inflammation and decrease the pain, however, it is not possible to use this treatment more than three times a year because there are too many side effects. These include risk of infection, water retention and elevated blood sugar levels, etc.
- Hyaluronic injections. Hyaluronic acid is a substance that is naturally present in the human body. It is found in the highest concentrations in fluids in the eyes and joints.
As we all understand, Osteoarthritis is characterized by a loss of articular cartilage and a reduction in the elastic and viscous properties of the synovial fluid occurs. The molecular weight and concentration of the naturally occurring hyaluronic acid decreases, which lead to decreases the lubrication and protection of the joint tissues of the knee.
The above theory raised the concept of viscosupplementation, i.e. injection of hyaluronic acid into the osteoarthritic knees.
One study from Canada showed that 80 percent of 458 knees injected with hylan had a positive response, and the average duration of efficacy was 8.2 months. (Lussier A, Cividino AA, McFarlane CA, Olszynski WP, Potashner WJ, De Medicis R. Viscosupplementation with hylan for the treatment of osteoarthritis: findings from clinical practice in Canada. J Rheumatol 1996;23:1579-85.)
Hyaluronic acid injection at your knee will provide lubrication for knee, acting as a lubricant and shock absorbent. The hyaluronic acid that is used as medicine is extracted from rooster combs or made by bacteria in the laboratory and similar to gelatinous material in the tissue spaces and generally throughout the body.
Side Effects of Hyaluronic Acid injection: No systemic reactions were attributed to hyaluronic acid. Most of the reported adverse reactions consisted of minor localized pain or effusion, which was almost always resolved within one to three days.
Indications of intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections:
- Significantly symptomatic osteoarthritis who have not responded adequately to standard nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic treatments.
- Intolerant of these therapies (e.g., gastrointestinal problems related to anti-inflammatory medications).
- Patients who are not candidates for total knee replacement or who have failed previous knee surgery for their arthritis, such as arthroscopic debridement, may also be candidates for viscosupplementation.
- Total knee replacement in younger patients may be delayed with the use of hyaluronic acid. As per current studies, the metal knee joint after total knee replacement may last 10 to 15 years, we usually recommend patients to have the total knee replacement in a older age, such as age of 65 or above to avoid two surgeries for total knee replacement in their life time. Therefore, by injection of hyaluronic acid into the knee joints, patient’s pain might decrease and the surgery might be delayed for a while.
Injection Technique
Hyalgan is supplied in 2-mL prefilled syringes. The recommended injection schedule is one injection per week for five weeks for Hyalgan. Repeat courses of Hyalgan can be performed after six months.
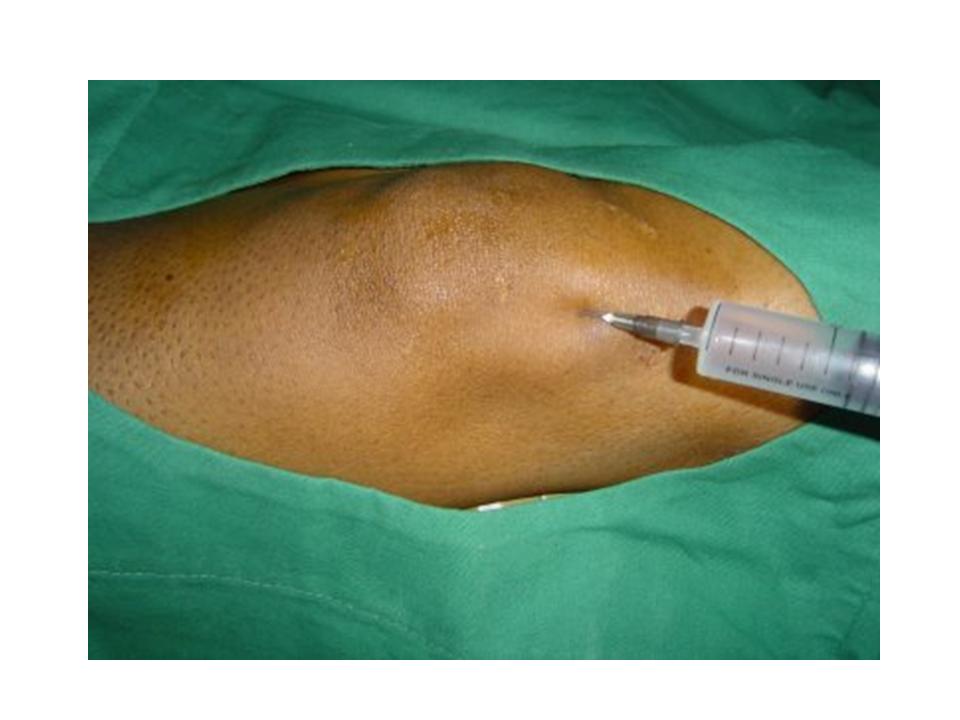
A knee joint can be injected several ways. One approach is to have the patient lie supine on the examination table with the knee flexed 60 to 90 degrees (Figure ). In this position, the anterior portions of the medial and lateral joint lines can easily be palpated as dimples just medial or lateral to the inferior pole of the patella. Often, the medial joint line is easier to palpate and define and can be chosen as the site of injection.
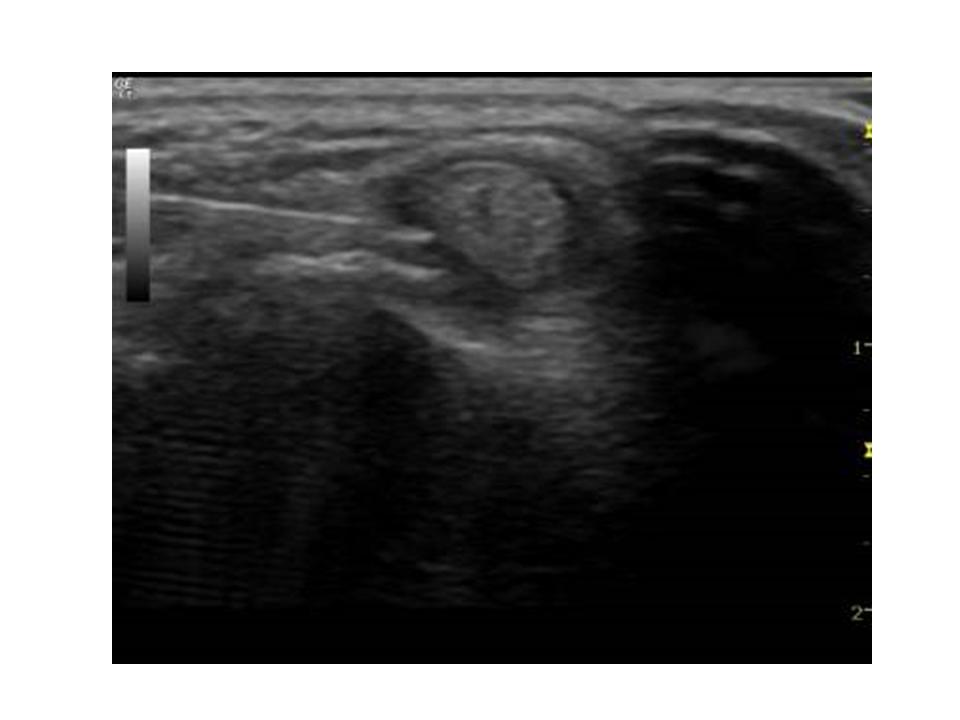
In my office, I routinely use ultrasound image to guide the knee injection, with this method, the injection is much more accurate and much less painful. If you would like to have knee injection, the ultrasound guided injection might give you a better result.
Fig. 4.16
Fig. 4.17
drericchan.wordpress.com
Fig. 4.18
www.myorthosports.com
- Surgery. There are two types of surgery:
- Arthroscopic surgery. This type will repair the torn meniscus, ligament and tendon.
- Total knee replacement. This operation is usually performed on people 65 and over, because the prosthetics of an artificial joint usually lasts only 15 to 20 years. If the replacement is performed too early, the patient might have to undergo another one at a later time.
Treatment by traditional Chinese medicine:
Traditional Chinese medicine has a long history of using acupuncture to treat knee arthritis. In western countries, acupuncture treatment of knee osteoarthritis has been intensively studied. Selfe TK, Taylor AG. Of University of Virginia collected ten trials representing 1456 participants met the inclusion criteria and were analyzed. These studies provide evidence that acupuncture is an effective treatment for pain and physical dysfunction associated with osteoarthritis of the knee. (Selfe TK, Taylor AG, Fam Community Health. 2008 Jul-Sep;31(3):247-54. Acupuncture and osteoarthritis of the knee: a review of randomized, controlled trials. School of Nursing and the Center for the Study of Complementary and Alternative Therapies, University of Virginia Health System, Charlottesville, VA 22908, USA.)
There are two major types of knee osteoarthritis:
- Wind hot: the knee is mild to moderate swollen, warm, or hot with severe tenderness
- Wind cold: the knee is very stiff, cold and heaviness, the pain is worse in the morning, difficulty moving, getting in or out of car, mild to moderate pain.
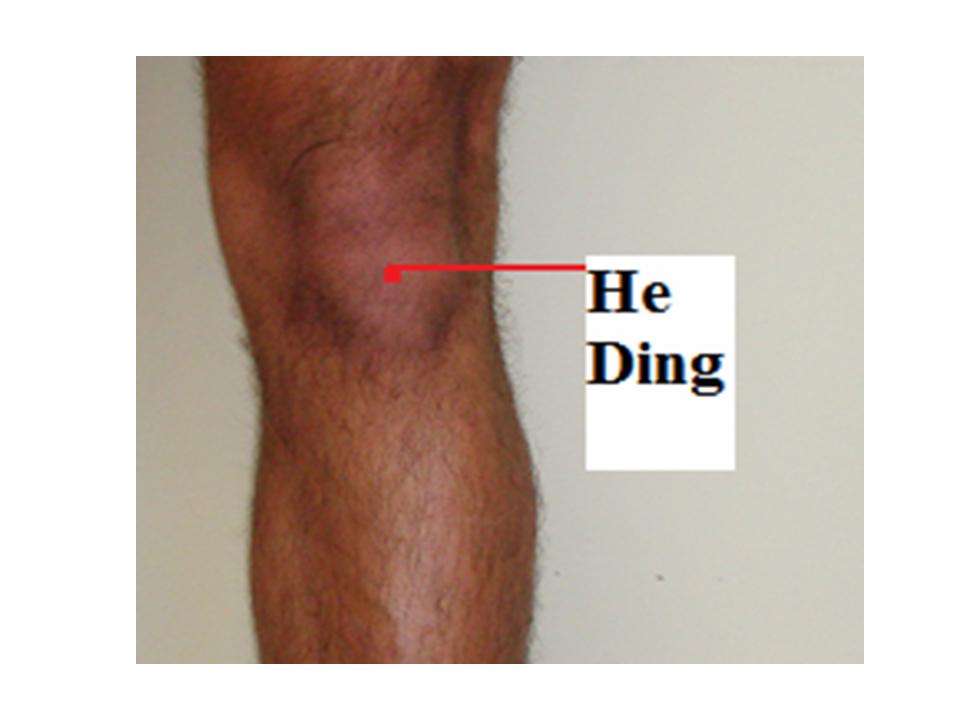
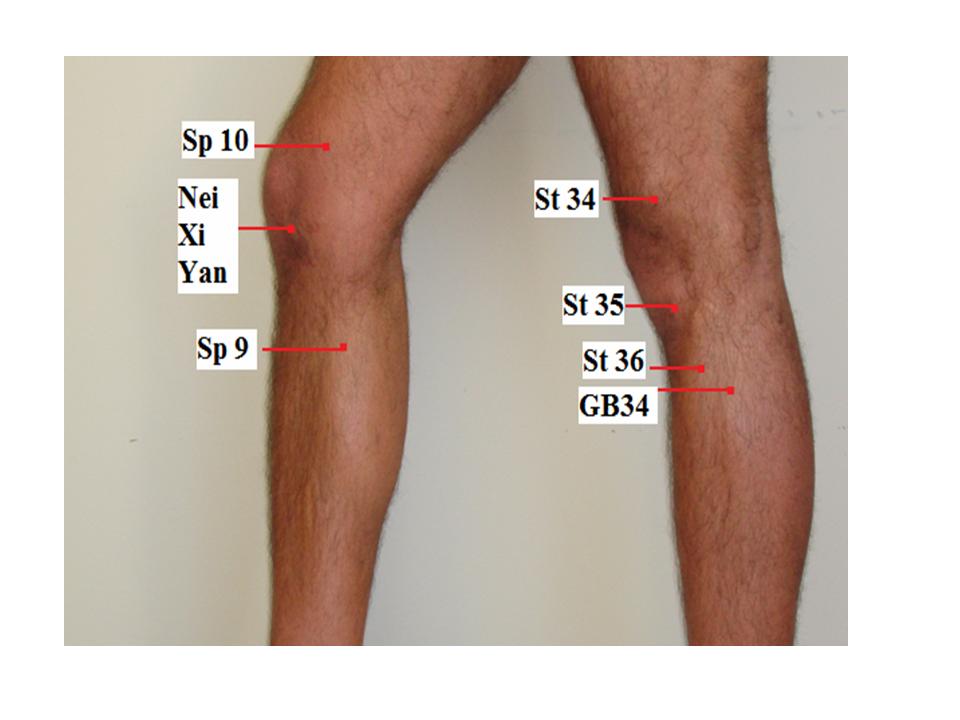
I choose the following acupuncture points for both type: St 35 Du Bi, Nei Xi Yan, Xue Hai, Liang Qiu, He Ding, Wei Zhong, I add Ying Ling Quan, Wei Yang for Wind hot, and Yang Ling Quan, Zhu San Li for Wind cold.
| Points | Meridan/No. | Location | Function/Indication | |
| 1 | Du Bi | Stomach 35 | When the knee is flexed, the point is at the lower border of the patella, in the depression lateral to the patellar ligament | Pain, numbness and motor impairment of the knee, beriberi |
| 2. | Nei Xi Yan | Extraordinarypoint | When the knee is flexed, the point is at the lower border of the patella, in the depression medial to the patellar ligament | Knee pain, weakness of the lower extremities |
| 3. | Xue Hai | Sp 10 | When the knee is flexed, 2 inch above the medial edge of patella. | Irregular menstruation, dysmenorrheal, uterine bleeding, amenorrhea, urticaria, eczema, erysipelas, pain in the medial aspect of the thigh |
| 4. | Liang Qiu | Stomach 34 | When the knee is flexed, the point is 2 inch above the laterosuperior border of the patella | Pain and numbness of the knee, gastric pain, mastitis, motor impairment of the lower extremities |
| 5. | He Ding | Extraordinarypoint | In the depression of the midpoint of the superior patellar border | Knee pain, weakness of the foot and leg, paralysis |
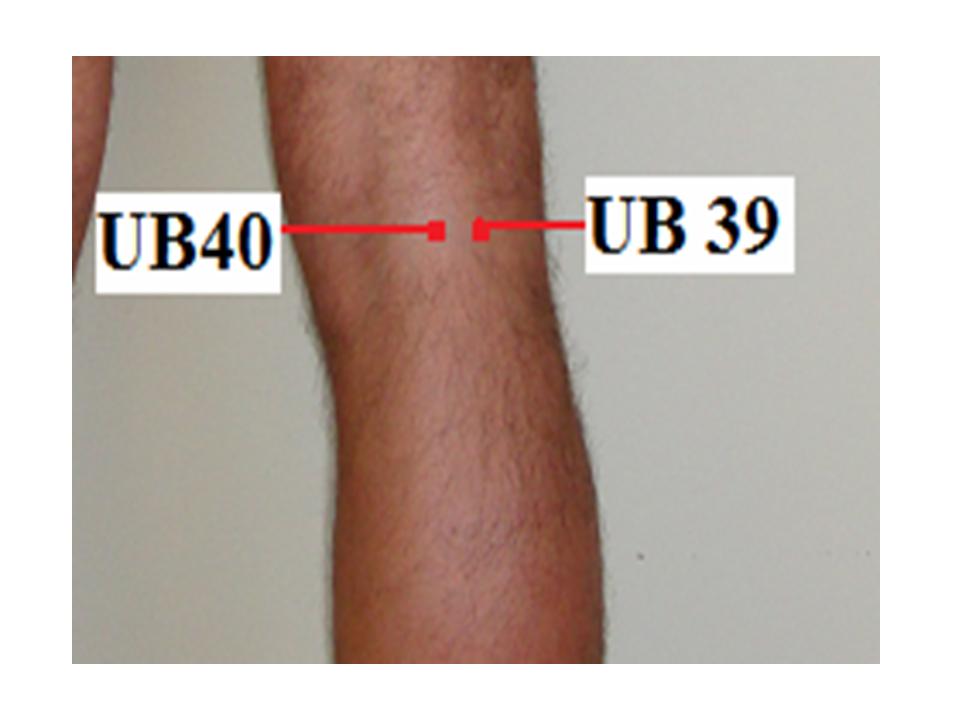
| 6. | Wei Zhong | UB 40 | Midpoint of the transverse crease of the popliteal fossa, between the tendons of biceps femoris and semitendinosus | Low back pain, motor impairment of the hip joint, lower extremities, contracture of the tendons in the popliteal fossa, muscular atrophy, pain, numbness of leg, hemiplegia, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, erysipelas. |
| 7. | Ying LingQuan | Sp 9 | On the lower border of the medial condyle of the tibia, in the depression on the medial border of the tibia | Abdominal pian and distension, diarrhea, dysentery, edema, jaundice, dysuria, enuresis, incontinence of urine, pain in the external genitalia, dysmenorrheal, pain in the knee |
| 8. | Wei Yang | UB 39 | Lateral to UB40, on the medial border of the tendon of biceps femoris | Stiffness and pain of the lower back, distension and fullness of the lower abdomen, edema, dysuria, cramp of the leg and foot |
| 9. | Yang Ling Quan | GB 34 | In the depression anterior and inferior to the head of the fibula | Hemiplegia, weakness, numbness and pain of the knee, beriberi, hypochondriac pain, bitter taste in the mouth, vomiting, jaundice, infantile, convulsion |
| 10. | Zu San Li | Stomach 36 | 3 inch below St. 35 Du Bi, one finger below the anterior crest of the tibia, in the muscle of tibialis anterior | Gastric pain, vomiting hiccup, abdominal distension, borborygmus, diarrhea, dysentery, constipation, mastitis, enteritis, aching of the knee joint and leg, beriberi, edema, cough, asthma, emaciation due to general deficiencyk, indigestion, apoplexy, hemiplegia, dizziness, insomnia, mia
|
Fig. 4.19
Fig. 4.20
Fig. 4.21
Jonathan underwent treatment with acupuncture, and his acute pain subsided and the swelling returned to normal after five sessions of acupuncture. I also injected Hyalgan once a week for five weeks. After the acupuncture treatments and injections, the patient reported that the pain was much subsided, and for almost a year he was pain free.
Tips for patients:
- Acupuncture and all other treatments besides surgery would buy you time if you have severe knee osteoarthritis. As I mentioned above, we recommended you have your total knee replacement as late as possible, the mechanical knee joint lasts only 10 to 15 years, you would not be happy during your life to have two times of total knee replacement.
- If you have mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis, acupuncture should be the first choice because of its effectiveness and no side effects.
- If you would like to consider Hyalgan or other Hyuaric Acid injection, you should ask your physician if they use ultrasound guided injection and if they inject your knee once a week for at least three weeks in your knee. I prefer to inject once a week for 5 weeks, which could guarantee you have enough Hyuaric Acid injected in your knee.
Tips for Acupuncturist:
- In the acute stage of any knee pain, the patient should be treated by old fashioned methods: protection, rest, ice, compression and elevation.
- If an acute ligament or meniscus injury is suspected, the patient should be referred to an orthopedic or rehabilitation physician and have a MRI for the knee.
- A recent study by the NIH showed acupuncture can significantly decrease the pain of knee osteoarthritis.
- After the acute phase subsides, acupuncture with Moxa is extremely effective for Wind cold type, acupuncture with ice at the knee is a very useful method for wind hot type.